5G Revolutionizes Supply Chain Automation: Manufacturing Enters a New Era of Precision and Profitability
- Last updated: December 01, 2025

- Technical Performance Specifications: Latency and Data Throughput
- Supply Chain Automation Applications and Case Studies
- Documented Cost Reduction Metrics and Financial Impact
- Network Architecture and Enabling Technologies
- Supply Chain Visibility and Inventory Management
- Implementation Challenges and Future Considerations
5G technology is fundamentally transforming supply chain automation in manufacturing through unprecedented improvements in latency, data throughput, and cost efficiency, with documented returns on investment exceeding 28 times initial capital expenditure and payback periods as short as three months. The deployment of 5G networks enables real-time machine-to-machine communication, autonomous systems coordination, and predictive maintenance that traditional connectivity solutions cannot support, resulting in measurable cost reductions ranging from 20% to 30% in maintenance expenses and up to 70% reductions in unplanned downtime across industrial facilities worldwide.
Technical Performance Specifications: Latency and Data Throughput
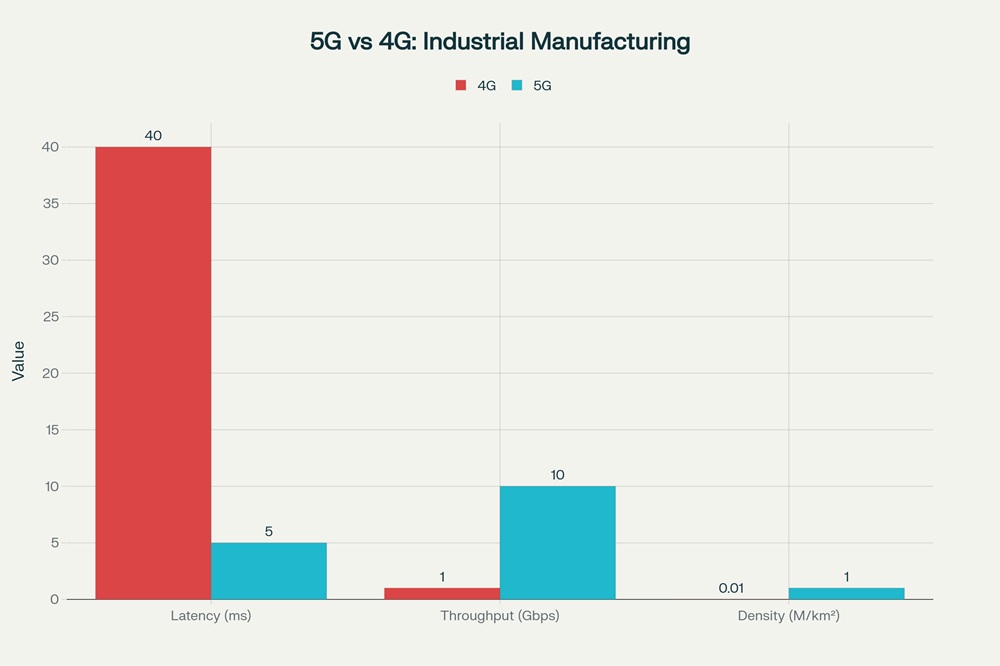
5G vs 4G: Key Performance Metrics for Industrial Manufacturing
The core technical advantages of 5G over previous generations represent the foundational enabler for supply chain automation breakthroughs. 5G networks achieve latency as low as 1 millisecond in ideal conditions, with real-world industrial deployments typically operating between 5 to 10 milliseconds—a stark contrast to 4G networks that operate at 30 to 70 milliseconds of latency. This latency reduction is critical for time-sensitive industrial applications; factory automation processes require latency between 0.25 milliseconds and 10 milliseconds to enable precise real-time control of machinery, and robotic motion control specifically demands cycle times of 2 milliseconds or less with a maximum one-way air interface delay of 500 microseconds. The responsiveness differential between 5G and 4G represents a 50-fold improvement in best-case scenarios and enables applications that were previously impossible with wireless connectivity.
In terms of data throughput, 5G delivers peak speeds of up to 10 to 20 gigabits per second, compared to 1 gigabit per second for 4G networks, with practical sustained speeds of 1 gigabit per second for most industrial applications. This enhanced bandwidth is essential for the high-volume sensor data collection and machine vision processing that characterizes modern smart factories. The Haier manufacturing facility, the world's largest white goods manufacturer, deployed 5G-enabled machine vision systems capable of inspecting refrigerators with 500-watt industrial cameras mounted on robotic arms, processing image data at rates previously impossible with prior network generations. The dramatic throughput improvement enables simultaneous connectivity to approximately one million IoT devices per square kilometer, representing a 100-fold increase over 4G's capacity, which translates to the deployment of sensor and monitoring systems at unprecedented density throughout manufacturing facilities.
The reliability and availability metrics of 5G networks also exceed previous generations, with availability reaching 99.99% or higher compared to 99.99% for 4G, but with significantly better performance under demanding industrial conditions. This reliability improvement is compounded by 5G's superior energy efficiency; 5G networks can accommodate 100 times more traffic while consuming less energy than previous generations through optimized spectral efficiency, wider bandwidths, and intelligent power-saving features.
Supply Chain Automation Applications and Case Studies
Real-time vehicle and asset tracking represents one of the most immediate applications of 5G in supply chain management. Automotive facilities monitor incoming component shipments through 5G connectivity, integrating tracking data directly into production workflows that automatically configure manufacturing lines based on real-time component arrival information. This eliminates the traditional inventory forecasting delays and enables just-in-time inventory strategies that reduce storage costs while maintaining production continuity. Logistics providers leverage 5G-enabled sensors on transportation vehicles to monitor location, speed, fuel consumption, and engine health continuously, enabling dynamic route optimization that reduces fuel costs and ensures timely deliveries in real time.
Autonomous systems coordination has emerged as a transformative application enabled by 5G's ultra-low latency. Automated mobile robots (AMRs) operating in warehouses communicate instantaneously with each other and central control units, avoiding collisions and optimizing routes in real time without the coordination failures that plagued Wi-Fi-dependent systems. Tesla's Gigafactory Texas facility (covering 12 million square feet) eliminated automated guided vehicle stoppages previously caused by unstable Wi-Fi connections through 5G deployment, while Tesla's Gigafactory Berlin-Brandenburg overcame up to 90% of overcycle issues in the General Assembly shop. These implementations demonstrate that 5G's reliability enables warehouses to deploy robotic systems throughout facilities rather than confining them to areas with reliable wired connections.
Predictive maintenance systems powered by 5G have delivered documented maintenance cost reductions of 25% to 30% and extended equipment lifespans by 20% to 40%. Real-time sensor monitoring of equipment temperature, vibration, pressure, and power consumption feeds into machine learning algorithms that identify developing equipment failures 2 to 8 weeks in advance, with failure prediction accuracy reaching 85% to 95%. This capability enables manufacturers to schedule maintenance during planned downtime windows rather than experiencing costly emergency failures. MTO Aero, an aerospace parts manufacturer producing turbine blade components (BLISKs) requiring approximately 100 hours of milling per part, deployed 5G vibration sensors that detected production issues within 1 millisecond, reducing rework rates from 25% to near zero and generating estimated annual savings of EUR 27 million for a single factory and EUR 360 million globally.
Quality control automation has achieved quantified improvements in defect detection and material yield. The Mercedes-Benz Factory 56 facility in Sindelfingen, Germany—the world's first 5G-connected automobile production facility covering 20,000 square meters—automated quality control testing directly on the production line, eliminating post-production testing requirements and significantly accelerating production timelines. Haier's refrigerator manufacturing facility eliminated manual defect inspection through 5G-enabled machine vision systems that scan units as they exit the production line with trained algorithms identifying exterior damage requiring replacement. Manufacturers implementing real-time quality monitoring have documented average defect rate reductions of 10% to 15% by identifying and correcting flaws as they emerge, with cloud quality control systems increasing testing capacity by 25%.
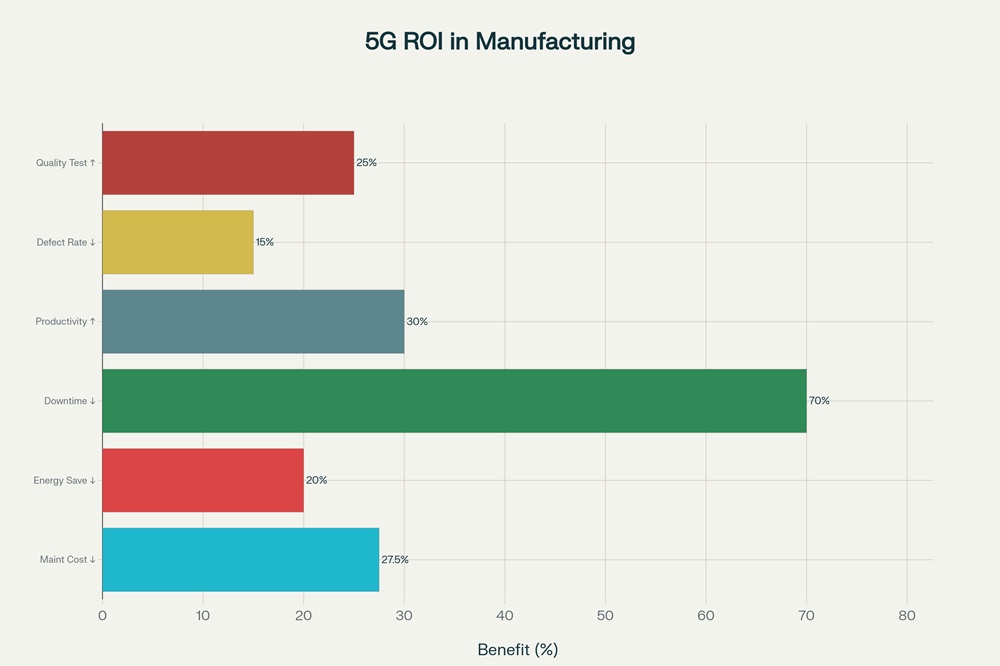
5G Manufacturing Impact: Cost Reduction and Efficiency Gains
Documented Cost Reduction Metrics and Financial Impact
The financial impact of 5G deployment in manufacturing has exceeded expectations across multiple verticals and facility sizes. Maintenance and operational cost reductions constitute the largest share of documented savings. ABI Research's qualitative discussions with manufacturing facilities documented energy savings of up to 20% and maintenance cost reductions of 25% to 30% driven by higher operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. The U.S. steel manufacturer utilizing Celona's 5G LAN infrastructure reduced unplanned downtime by more than 70 times, translating to over $2 million in annual material and labor cost savings, with the complete three-year subscription cost recouped in as little as three months. This facility reduced wireless access points by 4 to 6 times compared to Wi-Fi, lowering infrastructure costs and ongoing maintenance requirements significantly.
Productivity improvements directly attributable to 5G range from 15% to 42% across manufacturing facilities. A Purdue University study analyzing potential savings from deploying AT&T millimeter-wave 5G technology for data transmission from air compressor units estimated greenhouse gas emission reductions of 1,558.55 metric tons of CO2 equivalent annually per connected air compressor unit, with potential cumulative savings of 1.6 million metric tons of CO2 across 1,000 units. Manufacturers documented productivity gains of up to 30% by minimizing downtime and optimizing operations through 5G connectivity, with robust handovers enabling automated guided vehicles to operate at 30% higher speeds. Machine performance improvements of 15% became possible through real-time condition monitoring that identifies suboptimal equipment operation and automatically adjusts settings to maintain cycle speeds.
Return on investment timelines demonstrate the rapid financial payoff of 5G deployment. A comprehensive survey of 115 companies across five countries and multiple verticals revealed that 87% of industrial enterprises achieved measurable return on investment within 12 months of deploying private 5G networks, with 81% reporting lower setup costs than traditional connectivity alternatives and 86% documenting reduced ongoing operational costs. For critical equipment applications, ROI payback periods shortened to 6 to 12 months, while more comprehensive deployments requiring 18 to 24 months for optimization still demonstrated positive financial returns within this timeframe. These rapid payback periods occur because 5G deployments prevent unplanned downtime costs that typically exceed direct network investment savings by 3 to 5 times.
The macroeconomic impact projections underscore 5G's transformative potential for manufacturing. ABI Research projects that Tier 1 automotive suppliers and manufacturers can expect private 5G to generate $1 billion in cumulative value over five years, representing a 28-fold return on investment when analyzed across the automotive, electronics, and logistics sectors combined. The broader manufacturing industry is projected to gain $740 billion from 5G by 2030, with manufacturers expected to spend more than $1 billion on private 5G in 2025 alone, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 45.7%, surpassing $8.7 billion by 2030.
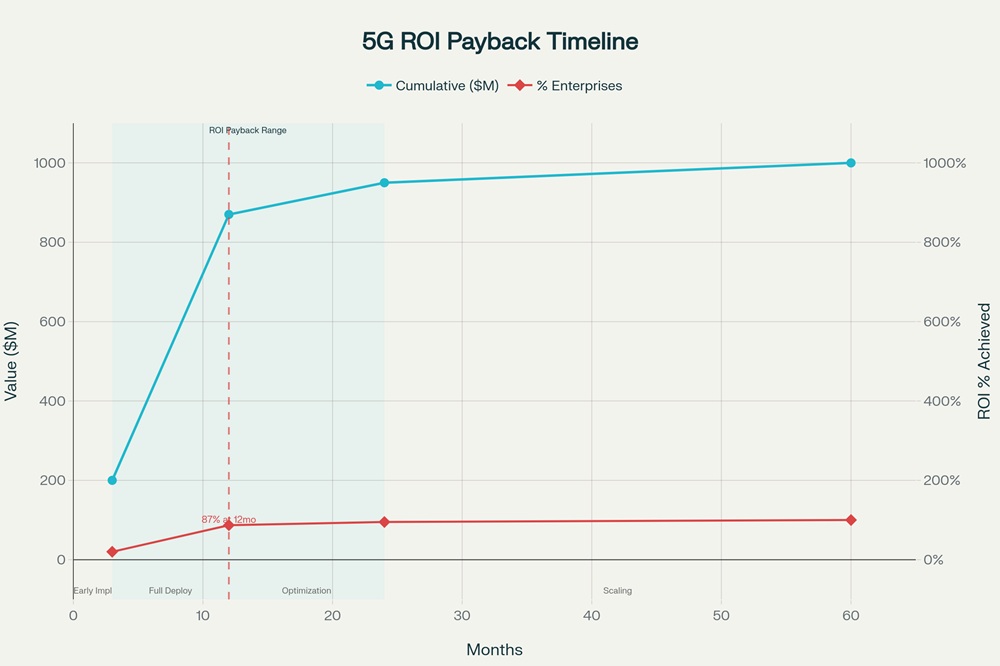
5G ROI Achievement Timeline in Manufacturing
Network Architecture and Enabling Technologies
Private 5G networks and network slicing have emerged as the preferred deployment architecture for manufacturing facilities, providing data sovereignty, enhanced security, and optimized performance for industrial applications. Private 5G networks enable organizations to operate dedicated mobile networks within their facilities, ensuring that sensitive production data remains secure and transmission latencies meet stringent industrial requirements. The Mercedes-Benz Factory 56 deployment with Ericsson and Telefonica Germany demonstrated that private 5G networks enable real-time production system interconnection while protecting proprietary manufacturing data from third-party exposure.
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) deployed alongside 5G creates a dual capability that maximizes latency reduction and processing efficiency. Edge computing infrastructure positioned on-premises processes data closer to its source, reducing round-trip delays that would occur with cloud-based processing. Haier's manufacturing facility achieved 5G MEC infrastructure installation and implementation in just 1.5 days compared to up to 35 days for legacy systems, enabling rapid deployment of new industrial applications. Network slicing, which divides a single physical 5G network into multiple virtual networks optimized for specific applications, allows manufacturers to allocate bandwidth and resources dynamically based on real-time production demands, ensuring critical manufacturing processes maintain required quality-of-service levels even during peak data transmission periods.
Supply Chain Visibility and Inventory Management
5G enables real-time supply chain transparency that was previously impossible with earlier network generations. Shipment location data, perishable goods condition monitoring, and inventory status become continuously available rather than episodic snapshots. Cold storage warehouses deploy 5G-connected sensors that continuously monitor and report temperature levels, immediately alerting managers to refrigeration equipment malfunctions that could compromise product integrity. Manufacturers receive real-time data on raw material status in transit and adjust production schedules accordingly, while retailers track goods movement from warehouses to store locations with visibility that ensures shelves remain properly stocked.
The integration of 5G tracking capabilities into just-in-time inventory strategies reduces both inventory carrying costs and the risk of stockouts or overstocking. Precision tracking reduces lead times and improves customer service reliability through dynamic supply chain adjustments based on real-time demand data. Autonomous trucks and delivery robots communicate through 5G with precision comparable to human operators, streamlining logistics operations and reducing delays that previously occurred through manual coordination.
Implementation Challenges and Future Considerations
Despite transformative benefits, 5G deployment in manufacturing faces persistent challenges. Infrastructure development costs remain significant, particularly in rural and remote areas where logistics operations increasingly operate. Cybersecurity concerns intensify as the proliferation of connected devices increases attack surface area, necessitating robust end-to-end encryption and comprehensive security protocols. The absence of global standards for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication creates integration complexity across different geographic regions and industrial systems. Smaller manufacturing companies face challenges affording the capital investment required for network upgrades and employee training to operate 5G-enabled systems effectively.
The standardization roadmap for industrial 5G continues evolving, with 3GPP R16 and R17 standards enhancing data speeds, latency specifications, and network capacity beyond current implementations. Future deployments will likely emphasize digital twin technology integration for simulation-based maintenance planning and edge AI processing that enables real-time predictions without cloud connectivity dependencies.
Conclusion
5G technology has transitioned from theoretical potential to demonstrated operational reality in manufacturing supply chain automation, delivering quantifiable improvements across latency (5-10 milliseconds vs. 30-70 milliseconds for 4G), data throughput (10-20 Gbps vs. 1 Gbps for 4G), and device density (1 million vs. 0.01 million per square kilometer). Cost reductions ranging from 20% to 30% in maintenance expenses, up to 70% in unplanned downtime, and productivity gains of 15% to 42% translate into measurable financial returns with 87% of industrial enterprises achieving ROI within 12 months. Tier 1 manufacturers project cumulative value generation of $1 billion over five years with 28-fold ROI multipliers. The convergence of 5G's technical capabilities with edge computing and network slicing creates a transformation in manufacturing automation that addresses legacy connectivity limitations while enabling autonomous systems, predictive maintenance, and real-time supply chain visibility that define Industry 4.0 manufacturing excellence.







