GPT-4.1 vs Llama 4 Maverick vs Gemini 1.5 Pro: Who Really Leads in Reasoning, Multimodality, and Speed in 2025?
- Last updated: December 01, 2025

GPT-4.1 vs Llama 4 Maverick vs Gemini 1.5 Pro
- Reasoning Capabilities and General Intelligence
- Multimodal Input Processing and Understanding
- Latency, Speed, and Real-Time Performance
- Long-Context Handling and Information Retrieval
- Coding and Software Engineering Performance
- Cost Efficiency and Deployment Considerations
- Architectural Innovations and Technical Specifications
- Practical Use Cases and Application Scenarios
- Limitations and Considerations
- Which model should you actually choose?
OpenAI's GPT-4.1, released in April 2025, represents the latest evolution in the GPT-4 series with significant improvements in coding capabilities, instruction following, and long-context understanding. Meta's Llama 4 Maverick, also released in April 2025, is the first open-source natively multimodal model utilizing a Mixture-of-Experts architecture with 17 billion active parameters out of 400 billion total parameters. Google's Gemini 1.5 Pro, launched earlier in February 2024 with subsequent updates, pushes the boundaries of long-context processing with support for up to 10 million tokens and near-perfect retrieval capabilities. These three models represent different approaches to advanced AI, each excelling in distinct areas while offering unique trade-offs in performance, cost, and capabilities.
Reasoning Capabilities and General Intelligence
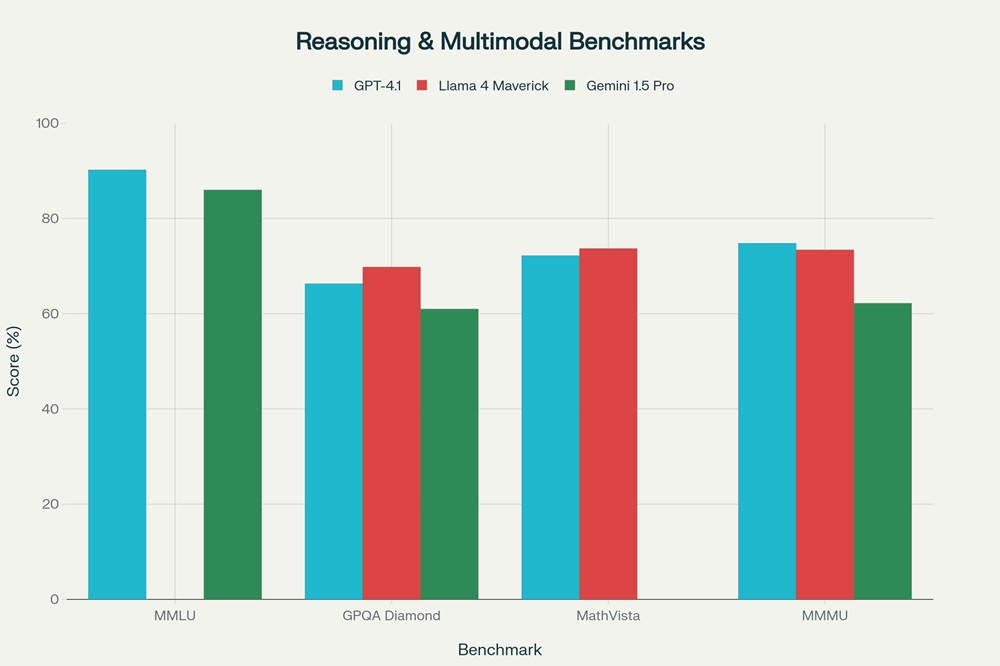
Comparison of reasoning and multimodal performance across GPT-4.1, Llama 4 Maverick, and Gemini 1.5 Pro on key benchmarks
GPT-4.1 demonstrates exceptional reasoning performance, achieving 90.2% on MMLU (Massive Multitask Language Understanding), outperforming both competitors in this comprehensive knowledge benchmark. The model scored 87.3% on Global MMLU, testing knowledge across multiple languages and cultures, demonstrating strong multilingual reasoning capabilities. On the AIME 2024 mathematics examination, GPT-4.1 achieved 48.1%, significantly outpacing Llama 4 Maverick's struggling 10-23% performance on mathematical problem-solving. This superior mathematical reasoning extends to instruction-following tasks, where GPT-4.1 scored 87.4% on IFEval and 38.3% on MultiChallenge, representing improvements of 10.5 percentage points over its predecessor GPT-4o.
Llama 4 Maverick shows competitive but more uneven reasoning performance across benchmarks. The model achieved 69.8% on GPQA Diamond, actually surpassing GPT-4.1's 66.3% on this graduate-level physics reasoning test. On MMLU Pro, a more challenging variant of MMLU, Maverick scored 80.5%, demonstrating solid reasoning capabilities despite lower scores on standard MMLU. However, the model's weakness in pure mathematical reasoning is evident in its AIME 2024 performance, where it scored only 10-23%, indicating struggles with multi-step symbolic reasoning. On IFEval, Maverick achieved a respectable 86%, nearly matching GPT-4.1's performance in instruction-following tasks.
Gemini 1.5 Pro maintains strong reasoning capabilities with 85.9-86% on MMLU, placing it between GPT-4.1 and Llama 4 Maverick. The model scored 61% on GPQA Diamond, lower than both competitors but still demonstrating solid graduate-level reasoning. Google's approach emphasizes using additional inference compute through majority voting, which can push MMLU performance to 91.7%, extending the performance ceiling beyond standard inference. On the MMMU (Massive Multitask Multimodal Understanding) benchmark, Gemini 1.5 Pro scored 62.2%, trailing GPT-4.1's 74.8% and Llama 4 Maverick's 73.4%, suggesting relatively weaker multimodal reasoning compared to the more recent models.
Multimodal Input Processing and Understanding
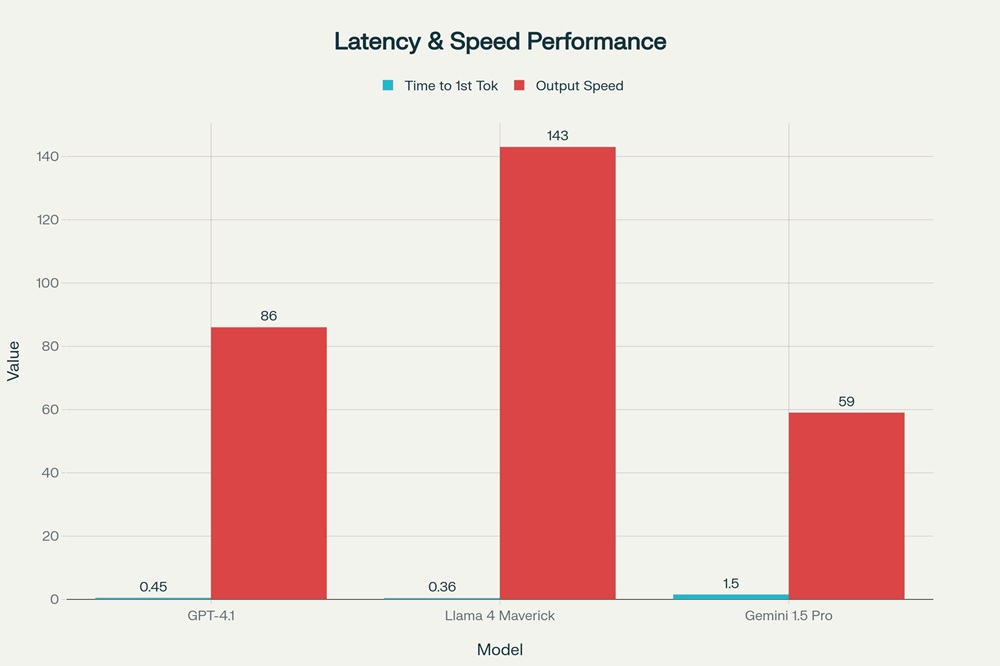
Comparison of latency (Time to First Token) and output speed across GPT-4.1, Llama 4 Maverick, and Gemini 1.5 Pro
GPT-4.1 excels in multimodal capabilities, particularly in video understanding where it achieved 72% on Video-MME (long videos without subtitles), analyzing 30-60 minute videos and improving 6.7% over GPT-4o. The model processes text, images, and video inputs seamlessly, with particularly strong image understanding capabilities scoring 74.8% on MMMU and 72.2% on MathVista, demonstrating excellent visual reasoning in mathematical contexts. GPT-4.1's multimodal embedding layers have been fine-tuned to better integrate complex multimodal data, enabling applications like analyzing long videos, processing extensive documents with images, and handling complex visual question-answering tasks. The model maintains these capabilities across its entire 1 million token context window with 100% retrieval accuracy in needle-in-haystack tests.
Llama 4 Maverick is Meta's first natively multimodal model, with early fusion mechanisms allowing comprehensive multimodal processing from initial stages. The model demonstrates exceptional document and chart understanding, scoring 90% on ChartQA and an outstanding 94.4% on DocVQA, significantly outperforming both competitors in visual document analysis. On MathVista, Maverick achieved 73.7%, slightly edging out GPT-4.1's 72.2% in visual mathematical reasoning. The model's MMMU score of 73.4% demonstrates strong general multimodal understanding. Maverick supports text, image, and video inputs, trained on over 30 trillion tokens of diverse data including text, images, and video stills, with the Mixture-of-Experts architecture using 128 experts where only 17 billion parameters are active per token.
Gemini 1.5 Pro was designed as a multimodal-first model, capable of processing text, images, video, and audio across its massive context window. However, its MMMU score of 62.2% trails both competitors, suggesting that while it handles multiple modalities, the quality of multimodal reasoning may not match the newer models. The model achieves near-perfect recall (>99%) on multimodal long-context retrieval tasks up to 10 million tokens, a capability neither GPT-4.1 nor Llama 4 Maverick can match. Gemini 1.5 Pro can process 1 hour of video, 11 hours of audio, or over 700,000 words in a single context window, enabling unique applications like learning new languages from grammar manuals or analyzing entire film-length videos without external retrieval systems.
Latency, Speed, and Real-Time Performance
Llama 4 Maverick dominates in speed and latency metrics, achieving the fastest Time to First Token (TTFT) of 0.36 seconds and output speeds of 125.6-160 tokens per second in standard deployments. On specialized hardware like the NVIDIA DGX B200 with eight Blackwell GPUs, Maverick can achieve extraordinary speeds exceeding 1,000 tokens per second per user, setting world records for LLM inference speed. The model's token-level inference speed ranges from 35 to 165 tokens per second depending on concurrency, with optimal performance at moderate concurrency levels. This exceptional speed makes Maverick ideal for real-time applications requiring low latency, such as interactive chatbots, live translation, and customer service applications where immediate responses are critical.
GPT-4.1 delivers moderate latency performance with TTFT ranging from 0.39 to 0.51 seconds across different deployments. The model achieves throughput of 40-132 tokens per second, with some measurements showing sustained output of 132.7 tokens per second, representing approximately 40% faster performance than GPT-4o. However, real-world deployment experiences vary significantly, with some users reporting 2-3 seconds for first token and occasional delays of 40+ seconds depending on query complexity and system load. The model's latency is generally lower than average compared to other large language models, making it suitable for most production applications though not as responsive as Llama 4 Maverick.
Gemini 1.5 Pro exhibits the slowest performance among the three models, particularly when processing long contexts. For standard inputs, the model generates approximately 59 tokens per second, significantly slower than both competitors. When processing large contexts approaching the million-token range, users report TTFT of 1-3 minutes, with one test showing 180.9 seconds (3 minutes) to process 1.76 million tokens before generating the first output token. However, Google has been actively working on optimizations, and more recent versions show improvements with sub-second first-token latency for smaller contexts and sub-10 second responses for moderately sized prompts. The Gemini 1.5 Flash variant offers much faster performance with 0.21-0.37 seconds TTFT and 163 tokens per second output speed, but sacrifices some reasoning quality.
Long-Context Handling and Information Retrieval
Gemini 1.5 Pro sets the gold standard for long-context processing with support for up to 10 million tokens in research settings and 1-2 million tokens in production. The model achieves >99% retrieval accuracy even at these extreme context lengths, maintaining 100% recall up to 530,000 tokens and >99.7% recall up to 1 million tokens in needle-in-haystack tests. This represents a generational leap over previous models, enabling processing of entire codebases with over 30,000 lines of code, multiple hours of video and audio, or complete document collections without external retrieval systems. The September 2024 update significantly improved practical long-context performance, with users reporting the model now effectively utilizes 23 times the context depth compared to earlier versions, though fully utilizing the entire 2 million token window remains challenging.
GPT-4.1 supports a 1 million token context window, representing an 8x increase over GPT-4o's 128,000 token limit. The model achieves 100% accuracy in needle-in-haystack retrieval tests across all context lengths, demonstrating reliable information extraction from massive documents. OpenAI specifically trained GPT-4.1 to "reliably attend to information across the full 1M context" and ignore irrelevant distractors, addressing a common failure mode of earlier long-context models. The model's long-context capabilities enable processing entire books, massive legal contracts, or multiple research papers simultaneously while maintaining reasoning quality, with no degradation in performance as context length increases.
Llama 4 Maverick also supports a 1 million token context window, matching GPT-4.1's capacity though with a more limited maximum output of 4,096 tokens compared to GPT-4.1's 32,768 tokens. While specific long-context retrieval benchmarks for Maverick are limited, the model's architecture incorporating iRoPE (improved Rotary Position Embeddings) enables effective context scaling and management. Meta's training approach included extensive long-context data from the 30+ trillion token training corpus, though the model does not reach Gemini's extreme context lengths. The 512,000 token context length mentioned in some deployments suggests production implementations may use shorter contexts than the theoretical maximum.
Coding and Software Engineering Performance
GPT-4.1 achieves state-of-the-art coding performance, scoring 54.6% on SWE-Bench Verified, a benchmark testing the ability to solve real GitHub issues in actual codebases. This represents a massive 21.4 percentage point improvement over GPT-4o's 33.2% and even surpasses the reasoning-focused o1 and o3-mini models. On code diff accuracy, GPT-4.1 achieved 52.9% compared to GPT-4o's 18.3%, demonstrating dramatically improved ability to modify only specific code sections rather than rewriting entire files. The model reduces extraneous code modifications to just 2% (down from 9% for GPT-4o), indicating more precise and targeted code changes. These improvements make GPT-4.1 particularly effective for agentic coding workflows, automated debugging, and large-scale codebase modifications.
Llama 4 Maverick demonstrates solid but less exceptional coding capabilities, scoring 43.4% on LiveCodeBench (problems from October 2024 to February 2025), a continuously updated benchmark using recent coding problems from platforms like LeetCode and CodeForces. This performance is respectable but falls short of GPT-4.1's achievements on more comprehensive coding benchmarks. On MBPP (Mostly Basic Python Programming), Maverick scored 77.6%, exceeding the previous generation Llama 3.1 405B's 74.4%, demonstrating improvements in basic programming tasks. The model achieves comparable results to DeepSeek V3 on reasoning and coding with less than half the active parameters (17B vs 37B), highlighting its efficiency though not necessarily superior raw performance.
Gemini 1.5 Pro shows moderate coding performance without the breakthrough improvements seen in GPT-4.1. While specific SWE-Bench scores are not widely reported, the model's coding capabilities are generally considered solid for general-purpose programming tasks. The model excels at code comprehension across massive codebases due to its long-context capabilities, able to process and understand over 30,000 lines of code simultaneously. This makes Gemini 1.5 Pro particularly effective for code review, codebase analysis, and documentation generation where understanding large code structures is more important than generating complex algorithms. However, for pure code generation tasks, Gemini appears to lag behind both GPT-4.1 and even Llama 4 Maverick in recent benchmarks.
Cost Efficiency and Deployment Considerations
Llama 4 Maverick offers the best cost efficiency with input pricing at $0.24 per million tokens and output pricing at $0.85 per million tokens through third-party API providers. This represents approximately 8x lower input costs and 9x lower output costs compared to GPT-4.1, making it the most economical option for high-volume applications. The model's open-source nature under the Llama 4 Community License Agreement provides additional deployment flexibility, allowing organizations to self-host on their own infrastructure. Meta designed Maverick to run on a single NVIDIA H100 DGX host, significantly reducing hardware requirements compared to dense models of similar capability. The Mixture-of-Experts architecture activates only 17 billion of the 400 billion total parameters per token, improving inference efficiency and reducing serving costs.
GPT-4.1 is priced at $2.00 per million input tokens and $8.00 per million output tokens, representing a 26% cost reduction compared to GPT-4o while delivering superior performance. OpenAI offers a 75% discount for cached inputs, making the model more economical for applications involving repeated prompts or large system messages. Despite not being open-source, GPT-4.1 is available through the OpenAI API with straightforward integration and enterprise-grade reliability. The model's pricing positions it in the mid-range category, more expensive than Llama 4 Maverick but comparable to other proprietary state-of-the-art models. For organizations prioritizing performance over cost and requiring minimal deployment complexity, GPT-4.1's pricing is competitive given its superior capabilities across most benchmarks.
Gemini 1.5 Pro is priced at $2.50 per million input tokens and $10.00 per million output tokens, making it the most expensive option among the three. However, Google has been reducing pricing over time while increasing rate limits and performance, with recent updates bringing down latency and improving throughput. The model is available through Google AI Studio and Vertex AI, offering enterprise features, security, and integration with Google Cloud services. For applications specifically requiring extreme long-context processing beyond 1 million tokens, Gemini 1.5 Pro's unique capabilities may justify the premium pricing. The Gemini 1.5 Flash variant offers a much more economical option at approximately $0.53 per million tokens blended price, providing 15x cost savings compared to Pro while maintaining much of the core functionality.
Architectural Innovations and Technical Specifications
GPT-4.1 employs a dense transformer architecture with advanced multimodal embedding layers that better integrate text, image, and video data. While OpenAI has not disclosed exact parameter counts, the model represents an iterative improvement over GPT-4, incorporating optimizations for instruction following, long-context attention, and code generation. The architecture includes mechanisms to "reliably attend to information across the full 1M context", suggesting specialized attention patterns or memory structures. GPT-4.1's training involved June 2024 knowledge cutoff data, making it relatively current compared to most competitors. The model family includes three variants: GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1 Mini, and GPT-4.1 Nano, offering different size/performance trade-offs.
Llama 4 Maverick utilizes a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, Meta's first release using this approach in the Llama series. The model contains 128 experts with only 2 experts active per token (plus one shared expert), totaling 17 billion active parameters out of 400 billion total parameters. The architecture uses alternating dense and MoE layers, with each token routed to the shared expert and one of the 128 routed experts, optimizing inference efficiency. Maverick incorporates 120 layers, 96 attention heads, 8 key-value heads using Grouped-Query Attention, and a hidden dimension size of 12,288. The model uses iRoPE for position embedding and RMS Normalization, enabling effective context scaling to 1 million tokens. Training involved approximately 22 trillion tokens with focus on multimodal data, followed by lightweight supervised fine-tuning and large-scale reinforcement learning emphasizing hard prompts and mixed-capability training batches.
Gemini 1.5 Pro employs a sparse Mixture-of-Experts Transformer architecture building on Gemini 1.0's multimodal foundation. The MoE approach allows the total parameters to grow while keeping activated parameters constant, enabling massive scale without proportional computational increases. While Google has not disclosed exact parameter counts, the model achieves comparable quality to Gemini 1.0 Ultra while using significantly less training compute and being significantly more efficient to serve. The architecture incorporates series of significant changes enabling long-context understanding up to 10 million tokens without degrading performance. Gemini 1.5 Pro underwent improvements across nearly the entire model stack including architecture, data, optimization, and systems, with particularly impressive advances in sparse and dense scaling techniques. The model is pre-trained on data including different modalities and instruction-tuned with multimodal data, with further refinement through human preference data.
Practical Use Cases and Application Scenarios
GPT-4.1 excels in scenarios requiring complex reasoning, advanced coding, and strong instruction following. Ideal applications include software development where the model's 54.6% SWE-Bench score enables effective automated code generation, debugging, and repository-level changes. The model's superior video understanding (72% Video-MME) makes it excellent for video analysis, content moderation, and multimedia education platforms requiring detailed comprehension of long-form video content. Enterprise applications benefit from GPT-4.1's balanced performance across reasoning, coding, and multimodal tasks, particularly for agentic workflows, complex document analysis combining text and images, and multi-step problem-solving. The model's 87.4% IFEval score makes it reliable for applications requiring precise instruction adherence, such as automated report generation, structured data extraction, and compliance-focused tasks.
Llama 4 Maverick is optimal for high-throughput, cost-sensitive applications requiring fast responses and excellent visual document understanding. The model's outstanding 94.4% DocVQA and 90% ChartQA scores make it ideal for document processing, data extraction from charts and tables, invoice analysis, and automated document understanding workflows. With the fastest latency (0.36s TTFT) and lowest cost ($0.24/$0.85 per million tokens), Maverick excels in real-time customer service, chatbots, live translation, and high-volume interactive applications. The model's open-source nature and single-GPU deployment capability make it perfect for on-premises deployments, organizations with data sovereignty requirements, and research institutions needing customization and fine-tuning capabilities. Applications requiring efficient multimodal processing without extreme performance demands benefit from Maverick's best-in-class performance-to-cost ratio.
Gemini 1.5 Pro uniquely serves applications requiring extreme long-context processing beyond what competitors can handle. The model's 10 million token capacity with >99% retrieval enables analyzing entire codebases, processing hours of video/audio content, comprehensive document collections review, and legal document analysis involving thousands of pages. Unique capabilities include in-context learning from entire books, such as learning to translate rare languages from grammar manuals alone, demonstrating few-shot learning capabilities impossible with shorter contexts. The model excels at research applications requiring synthesis across multiple long documents, regulatory compliance analysis, due diligence reviewing massive document sets, and content summarization of extensive multimedia libraries. While slower and more expensive, Gemini 1.5 Pro's unmatched long-context capabilities make it irreplaceable for specific applications where processing vast amounts of information in a single context is essential.
Limitations and Considerations
GPT-4.1 faces limitations in mathematical reasoning, with its 48.1% AIME score trailing human performance and raising questions about advanced mathematical problem-solving capabilities. The model's proprietary nature restricts customization and on-premises deployment, requiring dependence on OpenAI's API infrastructure. Some users report variable latency in production environments, with occasional delays of 40+ seconds suggesting capacity or load-balancing issues. The $2/$8 per million tokens pricing, while competitive for a proprietary model, is significantly more expensive than Llama 4 Maverick for high-volume applications. GPT-4.1's 32,768 maximum output tokens, while generous, may be insufficient for applications requiring generation of extremely long documents or code files.
Llama 4 Maverick struggles significantly with pure mathematical reasoning, scoring only 10-23% on AIME 2024, revealing weaknesses in multi-step symbolic reasoning and complex problem-solving. The model's coding performance (43.4% LiveCodeBench) lags substantially behind GPT-4.1's 54.6% SWE-Bench score, making it less suitable for advanced software engineering tasks. The 4,096 token maximum output is restrictive compared to GPT-4.1's 32,768 tokens, limiting applications requiring long-form generation. While open-source provides flexibility, it also means users bear responsibility for deployment, scaling, monitoring, and maintaining model infrastructure. Some benchmarks suggest Maverick is "LMArena maxed", potentially indicating optimization for specific benchmarks rather than broad real-world performance. The model's performance on complex reasoning tasks doesn't quite match GPT-4.1 or premium proprietary models.
Gemini 1.5 Pro exhibits the slowest performance among the three models, particularly problematic for real-time applications, with 1-3 minute TTFT for long contexts making it unsuitable for interactive use cases. The model's MMMU score of 62.2% is significantly lower than both competitors, suggesting weaker multimodal reasoning despite supporting multiple input types. Practical long-context utilization remains challenging, with users reporting the model doesn't fully utilize the entire 2 million token window effectively, though improvements continue. The highest pricing ($2.50/$10 per million tokens) among the three models makes it expensive for high-volume applications, though justified for specific long-context requirements. Some benchmarks show Gemini performing worse than competitors on certain tasks like coding and focused multimodal reasoning, despite its impressive long-context capabilities.
Which model should you actually choose?
Putting all of this together, the choice is less about “who is the winner” and more about fit to workload:
- If you are building a coding assistant, complex reasoning agent, or high-stakes enterprise automation where correctness and instruction following matter most, GPT-4.1 is currently the strongest all-round choice.
- If your priority is cost, latency, and heavy document/visual workloads—customer support bots, invoice processing, chart/report understanding, or large-scale chat deployments—Llama 4 Maverick offers exceptional value and speed.
- If your product fundamentally depends on extreme-long-context reasoning—multi-million token analysis, full codebase comprehension, or cross-document research over massive archives—Gemini 1.5 Pro is uniquely capable, despite its higher cost and slower responses.
In 2025, these three models together sketch the frontier of general-purpose AI: one optimized for quality, one for speed and openness, and one for sheer context scale. For builders, the real opportunity lies in understanding these trade-offs deeply, and then assembling the right mix—using each model where its strengths matter most.







